
The ellipses represent the use cases, which are descriptions of valuable work that can be performed with the system. (These can even be other computer systems, as is the case with “ATM.”) The box represents the boundary of your system. Use case diagrams are intentionally simple to prevent you from getting bogged down in system implementation details prematurely.Įach stick person represents an “actor,” which is typically a human or some other kind of free agent. You can think of a scenario as a question that starts with: “What does the system do if.?” For example, “What does the auto-teller do if a customer has just deposited a check within the last 24 hours, and there’s not enough in the account without the check having cleared to provide a desired withdrawal?” Each of these “situations” is referred to as a scenario, and a use case can be considered a collection of scenarios. "If you are designing an auto-teller, for example, the use case for a particular aspect of the functionality of the system is able to describe what the auto-teller does in every possible situation. This example of bank ATM UML activity diagram was created on the base of UML use case diagram of automated teller machine from the course "Thinking in Java, 2nd edition, Revision 9" by Bruce Eckel published on the website of the Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department of the University of Maryland, Baltimore (UMBC).
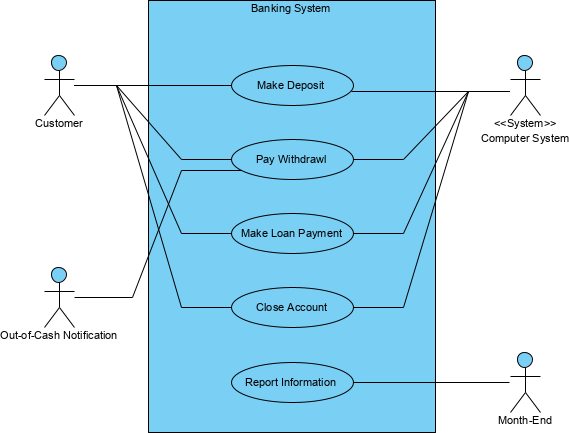
The UML use case diagram example "Banking system" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Rapid UML solution from the Software Development area of ConceptDraw Solution Park.
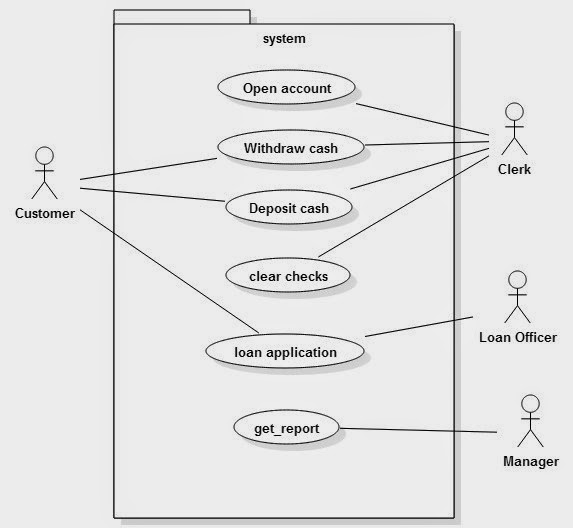
Its main job is to increase the customer base for the bank." (10) DSA is a Direct Selling Agent, who works for the bank based on a contract. Video banking can be performed via purpose built banking transaction machines (similar to an Automated teller machine), or via a video conference enabled bank branch clarification. (9) Video banking is a term used for performing banking transactions or professional banking consultations via a remote video and audio connection. (8) Telephone banking is a service which allows its customers to conduct transactions over the telephone with automated attendant or when requested with telephone operator.
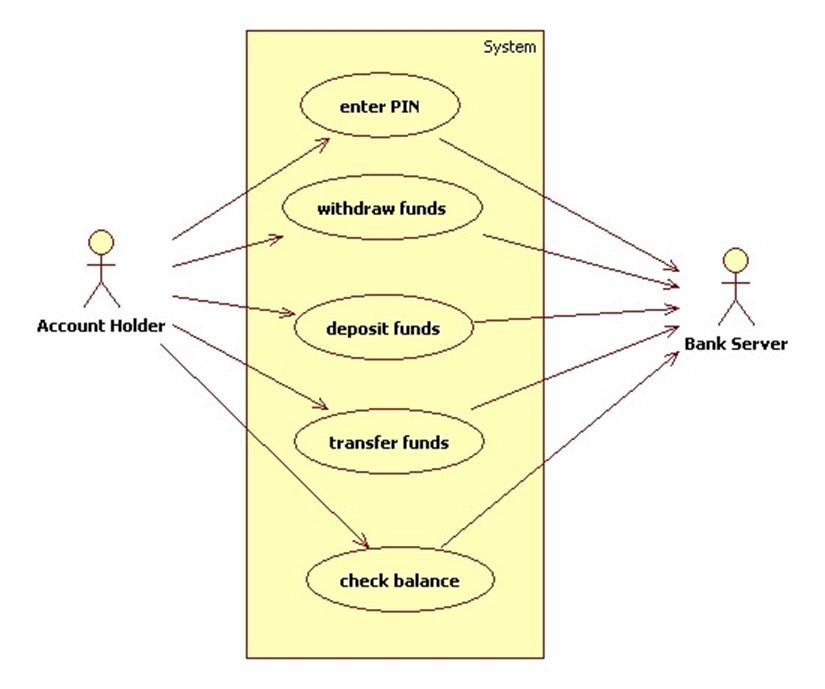
(7) Relationship Managers, mostly for private banking or business banking, often visiting customers at their homes or businesses. (6) Online banking is a term used for performing multiple transactions, payments etc. (5) Mobile banking is a method of using one's mobile phone to conduct banking transactions. (4) Mail: most banks accept cheque deposits via mail and use mail to communicate to their customers, e.g. "Banks offer many different channels to access their banking and other services:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
